Clean-in-Place (CIP) Cleaning
Jul 24,2025
Keeping things clean is a big deal in industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and beverages, where hygiene directly impacts safety and quality. That’s where Clean-in-Place (CIP) comes in. CIP allows cleaning equipment without taking it apart. It’s efficient, reliable, and ensures that equipment stays hygienic without causing downtime.
What Does CIP Cleaning Mean?
Clean-in-Place (CIP) means cleaning equipment without disassembling it. Instead of manually cleaning every part, CIP involves circulating cleaning solutions through the system to sanitize it. The process uses a mix of water, cleaning agents, heat, and pressure to remove dirt, bacteria, and residue. It’s automated, meaning it’s fast and reliable, and it also saves on cleaning supplies and water.
History of CIP
CIP started in the 1950s, mainly in the dairy industry. Back then, manual cleaning took a lot of time and was inefficient. The invention of CIP made cleaning faster, and it helped dairy producers avoid long shutdowns. Over the years, other industries like brewing, pharmaceuticals, and food processing started using it, and now it’s a standard process for many businesses that require strict hygiene.
Why Is CIP Cleaning Important?
CIP cleaning is important because it keeps things safe and efficient:
- Hygiene First: CIP ensures that equipment stays free of bacteria, ensuring safe, clean products.
- Less Downtime: With CIP, you don’t have to stop the whole operation to clean. Everything stays in place, so production runs smoothly.
- Cost-Effective: The cleaning solutions can be reused, saving both money and resources.
- Consistency: Automated systems mean every part of the equipment gets cleaned the same way every time.
- Eco-Friendly: CIP systems are designed to use cleaning agents and water efficiently, helping businesses reduce waste.
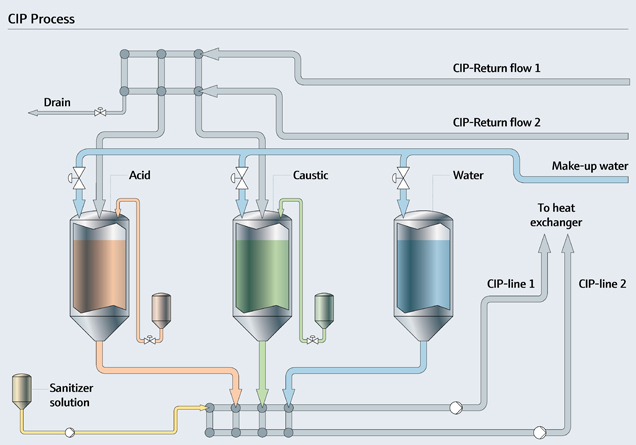
CIP Cleaning Process Overview
CIP cleaning process involves circulating cleaning solutions through the system, ensuring hygiene and reducing downtime.
CIP Process Steps
- Pre-rinse: Water is used to remove loose debris and residues.
- Cleaning Solution Circulation: Alkaline or acidic cleaning agents break down dirt, grease, and bacteria.
- Rinse: Water removes cleaning agents.
- Sanitisation: Hot water or steam kills bacteria and pathogens.
- Final Rinse: Clean water removes remaining residues.
CIP System Types
There are two main types of CIP systems: Single-Use Systems and Recycling Systems.
Single-use systems are designed for one-time use, where cleaning solutions are discarded after each cycle. These systems are ideal for smaller operations or individual loops, as they don’t require complex setup or storage for cleaning solutions.
On the other hand, Recycling Systems stores cleaning solutions for reuse in subsequent cleaning cycles. This makes them cost-effective and environmentally friendly, as they reduce the need for new cleaning agents and water with each cycle. These systems are more suitable for larger-scale operations where multiple cleaning cycles are needed.
CIP Cleaning Solutions
- Alkaline Solutions: For organic material removal (grease, fats).
- Acidic Solutions: For mineral build-up (scale, calcium).
- Sanitisers: Ensure equipment is free from harmful bacteria.
Key Considerations for CIP
- Select the right cleaning solution.
- Control temperature and flow rates.
- Minimise chemical and water use for sustainability.
Picture from endress.com
Industries that Use CIP
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, maintaining cleanliness ensures safe and high-quality products. CIP is widely used to clean production lines, tanks, pipes, and vessels without the need for disassembly. It helps prevent contamination by bacteria and allergens, ensuring that food products meet regulatory standards and are safe for consumption. For example, breweries use CIP to clean fermentation tanks and production lines, while juice manufacturers use it to clean mixing and packaging systems.
Pharmaceutical Industry
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, CIP prevents contamination of products that must adhere to strict hygiene and safety regulations. CIP systems are used to clean equipment like mixers, reactors, and packaging machines, ensuring that no residue or harmful substances remain. This is especially important in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and vaccines, where even the smallest trace of contamination could affect efficacy or safety. CIP also ensures compliance with industry standards like GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) and FDA regulations.
Dairy Industry
In dairy production, CIP maintains hygiene, ensuring that milk, cheese, yoghurt, and other dairy products are free from harmful bacteria and pathogens. CIP is used to clean equipment like pasteurizers, homogenisers, and storage tanks, preventing contamination that could lead to foodborne illnesses. Regular CIP cleaning in dairy plants ensures that production is efficient and safe, reducing the risk of spoilage and improving the shelf life of dairy products.
Beverage Industry
CIP is extensively used in the beverage industry to maintain the cleanliness of production lines and equipment, particularly in breweries, soft drink plants, and bottling facilities. It ensures that equipment such as fermentation tanks, mixers, and filling machines are sanitized to prevent contamination from yeast, bacteria, or other pathogens. CIP also helps preserve the flavor and quality of beverages, ensuring that they meet health standards and customer expectations.
Cosmetics Industry
In the cosmetics industry, CIP systems are used to clean mixing vessels, pipelines, and filling equipment, preventing cross-contamination between different product batches. The use of CIP in cosmetics manufacturing helps maintain product consistency, quality, and safety.
Each of these industries benefits from CIP by improving operational efficiency, reducing downtime, maintaining high hygiene standards, and ensuring regulatory compliance. By automating the cleaning process, CIP not only saves time but also ensures consistent and reliable sanitation across various stages of production.
What to Look Out For?
When running CIP, keep these things in mind:
- Choose the Right Cleaning Solution: Make sure the cleaning agent is suitable for what you need to clean.
- Control Temperature: Get the right heat for effective cleaning.
- Check Flow and Pressure: Ensure the solution is circulating correctly to clean all surfaces.
- Proper Rinsing: Ensure thorough rinsing to remove all chemicals.
- Track Everything: Record temperature, time, and chemical concentrations for safety and compliance.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep an eye on the system to ensure it works as expected.
Validate: Periodically check to make sure your CIP process meets all the required standards.
--- END ---
Prev: Sterilization in Place
Next: Abrasive Materials